Tech
Adenoidid: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
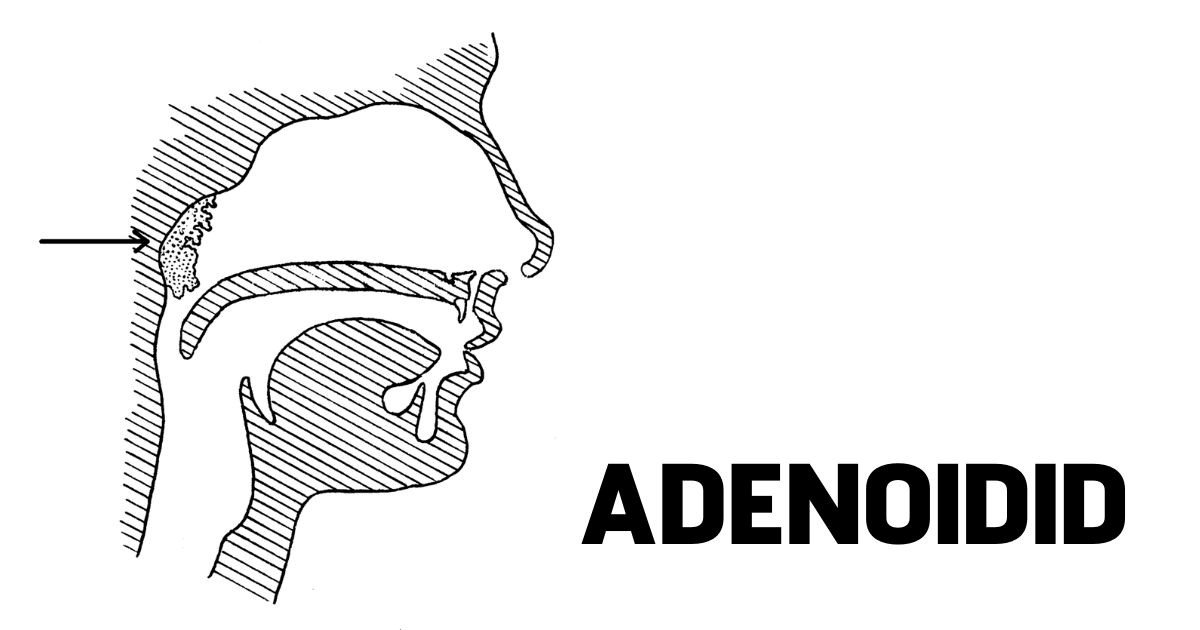
Adenoidid, more commonly known as adenoiditis, is a medical condition that affects the adenoids, small lymphatic tissues located behind the nose. These tissues play a vital role in the immune system, especially in children, by trapping bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose and mouth. However, when the adenoids become swollen or infected, it can lead to discomfort and complications in breathing, hearing, and overall health. This article explores adenoidid in detail—its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatments—to help you understand how to manage and prevent this condition.
What Are Adenoids?
Adenoids are part of the body’s immune defense system, situated high in the throat behind the soft palate. They work alongside the tonsils to trap harmful germs. While they are important in early childhood, adenoids usually shrink as a child grows older and may disappear entirely by adulthood. However, when they become infected or inflamed, they can cause significant discomfort and health issues.
Understanding Adenoidid
Adenoidid refers to the inflammation or infection of the adenoids. This condition is more common in children than in adults due to their developing immune systems. The infection may result from bacterial or viral causes, often following upper respiratory infections. If left untreated, adenoidid can lead to chronic breathing difficulties, ear infections, or sleep problems.
Causes of Adenoidid
Several factors can trigger adenoid inflammation.
- Bacterial infections: Streptococcus and other bacteria often infect the adenoids, causing swelling and pain.
- Viral infections: Common cold viruses like adenoviruses and rhinoviruses can lead to adenoid inflammation.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to dust, pollen, or mold may cause chronic irritation of the adenoids.
- Recurrent throat infections: Frequent infections can weaken the adenoids, making them prone to inflammation.
Environmental factors, such as pollution or exposure to secondhand smoke, can also worsen adenoid swelling.
Symptoms of Adenoidid
The symptoms of adenoidid can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation. Common signs include:
- Nasal congestion or difficulty breathing through the nose
- Snoring or noisy breathing during sleep
- Mouth breathing
- Sore throat and dry mouth
- Recurrent ear infections or ear pain
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- Nasal-sounding voice
In severe cases, chronic adenoiditis may cause sleep apnea or difficulty swallowing.
How Adenoidid Affects Children
Children are more susceptible to adenoidid because their adenoids are relatively larger and more active. Persistent infections can interfere with their sleep, hearing, and growth. Chronic mouth breathing may even affect facial development, leading to what is known as “adenoid facies,” characterized by a long face, open mouth, and dental issues. Early detection and treatment are essential to avoid such complications.
Diagnosis of Adenoidid
Diagnosing adenoidid requires a thorough medical examination. Doctors may use the following methods:
- Physical examination: A doctor may check the throat and ears for signs of infection.
- Nasal endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera helps visualize the size and condition of the adenoids.
- X-rays: Imaging can reveal whether the adenoids are enlarged.
- Lab tests: In some cases, a throat culture or swab may be done to identify the type of infection.
Accurate diagnosis is key to determining the right treatment approach.
Complications of Untreated Adenoidid
If adenoidid is not properly managed, it can lead to several complications, including:
- Chronic ear infections (otitis media)
- Hearing loss due to fluid buildup behind the eardrum
- Difficulty sleeping or sleep apnea
- Chronic sinus infections
- Speech and facial growth problems in children
Ignoring these symptoms may result in long-term health issues, so medical attention should not be delayed.
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
The treatment for adenoidid depends on the cause and severity of the condition.
- Medication: Antibiotics are often prescribed for bacterial infections, while decongestants and pain relievers can ease symptoms.
- Home care: Staying hydrated, inhaling steam, and using saline nasal sprays can help reduce congestion.
- Allergy management: If allergies are the cause, antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids may be recommended.
- Surgery (Adenoidectomy): In chronic or severe cases, surgical removal of the adenoids may be necessary, especially if the condition causes breathing or hearing problems.
Most children recover quickly from adenoid removal, and it rarely affects the immune system.
Adenoidectomy: What to Expect
An adenoidectomy is a minor surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia. It usually takes less than an hour, and most children can return home the same day. Recovery typically involves mild sore throat and discomfort for a few days. The benefits of surgery include improved breathing, better sleep, and fewer infections.
Preventing Adenoidid
Prevention is always better than cure. To reduce the risk of adenoid infections:
- Encourage regular handwashing to prevent the spread of germs.
- Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke and pollution.
- Treat allergies promptly.
- Maintain good oral and nasal hygiene.
- Ensure a healthy diet rich in vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
These preventive steps can minimize the chances of recurrent adenoid infections.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if your child:
- Has frequent nasal congestion or ear infections
- Snores excessively or breathes through the mouth during sleep
- Experiences persistent sore throat or difficulty swallowing
- Shows signs of fatigue and poor concentration due to sleep problems
Prompt diagnosis ensures effective treatment and prevents complications.
Adenoidid in Adults
Although rare, adenoidid can occur in adults due to chronic infections, allergies, or other underlying health conditions. Symptoms may resemble sinus infections, making diagnosis challenging. Adults with persistent nasal or throat issues should seek medical advice to rule out adenoid enlargement or other disorders.
Recovery and Long-Term Outlook
Most cases of adenoidid respond well to treatment. After medical or surgical intervention, symptoms like nasal blockage and snoring typically improve within days. Long-term outcomes are excellent, especially when preventive measures are followed. Once treated, children often experience better sleep quality, improved breathing, and overall enhanced well-being.
Conclusion
Adenoidid is a common yet manageable condition that primarily affects children but can also occur in adults. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. Whether managed medically or surgically, recovery from adenoidid is generally quick, and outcomes are positive. By maintaining good hygiene, managing allergies, and seeking timely medical care, you can help ensure a healthy respiratory system and a better quality of life.
FAQs
1. What is adenoidid?
Adenoidid, also known as adenoiditis, is the inflammation or infection of the adenoids—lymphatic tissues located behind the nose.
2. What causes adenoidid?
It is usually caused by bacterial or viral infections, allergies, or exposure to irritants like smoke or pollution.
3. How is adenoidid treated?
Treatment may include antibiotics, nasal sprays, and in severe cases, surgical removal of the adenoids (adenoidectomy).
4. Is adenoid removal safe?
Yes, adenoidectomy is a common and safe procedure with minimal risks and a quick recovery period.
5. Can adults get adenoidid?
Although rare, adults can develop adenoidid due to chronic infections or allergies, and it requires medical evaluation.
Tech
Yalla Choy: Meaning, Usage, and Cultural Context
The phrase yalla choy may sound playful or confusing at first, especially if you hear it in casual conversation or online. It blends familiar sounds from different languages, which is exactly why it stands out. People use it to express urgency, humor, or shared understanding without stopping to explain. To truly grasp yalla choy, it […]

The phrase yalla choy may sound playful or confusing at first, especially if you hear it in casual conversation or online. It blends familiar sounds from different languages, which is exactly why it stands out. People use it to express urgency, humor, or shared understanding without stopping to explain. To truly grasp yalla choy, it helps to look beyond literal translation and focus on how people actually use it.
Understanding What Yalla Choy Means
Yalla choy does not have a strict dictionary definition, and that is part of its charm. The phrase feels conversational, often used to signal action, agreement, or a light push forward. Its meaning shifts slightly depending on tone, setting, and who is saying it.
In practice, people use yalla choy the way they use friendly nudges in speech. It can mean let’s go, hurry up, or come on, but without sounding harsh.That softness makes it useful in relaxed or familiar environments.
The value of the phrase lies in emotion rather than precision. It communicates mood and intention more than exact instruction. That emotional clarity often matters more than literal meaning in real conversations.
Linguistic Roots and Influences
The phrase yalla is widely known from Arabic-speaking cultures, where it commonly means let’s go or hurry. Choy, on the other hand, appears in South Asian and informal slang contexts, often used as a casual call or exclamation.
When combined, yalla choy reflects how languages blend in multicultural spaces. People naturally mix words they hear daily, especially in cities or online communities where multiple languages coexist.
This blending is not random. It happens because speakers want expressions that feel natural and expressive. Yalla choy survives because it sounds friendly, energetic, and familiar across cultural lines.
How Yalla Choy Is Used in Daily Speech
In everyday conversation, yalla choy is often used among friends or peers. It might be said when encouraging someone to move faster or join in without pressure. The phrase keeps things light and avoids sounding commanding.
Tone plays a big role here. Said with a smile, it feels inviting. Said jokingly, it can ease tension or add humor. The flexibility of tone makes it adaptable to many social situations.
Because it feels informal, people rarely use it in professional settings. Its strength lies in casual interaction, where warmth and shared understanding matter more than correctness.
Role of Informal Phrases in Modern Culture
Phrases like yalla choy show how language evolves to meet social needs. Modern communication values speed, relatability, and emotional clarity. Informal expressions often deliver all three more effectively than formal speech.
These phrases also help build group identity. When people share a way of speaking, they feel connected. Using the same expressions creates a sense of belonging without needing explanation.
In this way, yalla choy is more than words. It becomes a social signal, showing familiarity, friendliness, and cultural overlap in everyday interaction.
Online and Social Media Usage
Social media has given phrases like yalla choy a wider stage. Short, expressive terms work well in comments, captions, and messages where space and attention are limited. They convey tone quickly without long explanations.
Online usage often amplifies humor. People may use the phrase playfully in memes or casual replies. This keeps the expression alive and relevant, especially among younger users.
Digital spaces also encourage experimentation. New phrases appear, disappear, or evolve rapidly. Yalla choy fits this environment because it is flexible and easy to adapt.
Why Such Expressions Spread So Easily
The spread of yalla choy is driven by simplicity and sound. It is easy to say, easy to remember, and pleasant to hear. These qualities help any phrase travel faster through conversation.
Another factor is emotional usefulness. The phrase fills a gap between being too serious and too vague. It communicates intent without pressure, which people appreciate in social interactions.
Finally, shared exposure matters. Hearing a phrase repeatedly from friends or online makes it feel normal. Over time, repetition turns novelty into habit.
Common Misunderstandings About the Phrase
Some people assume yalla choy has a fixed or literal translation. This can lead to confusion when they try to define it too rigidly. In reality, its meaning depends heavily on context.
Others think such phrases are careless or incorrect language use. However, informal expressions play a real role in communication. They carry tone, emotion, and social cues that formal language often misses.
Understanding this helps avoid misjudgment. Instead of asking what it strictly means, it is more useful to observe how and when people use it.
Conclusion
Yalla choy is a small phrase with a big social role. It reflects cultural blending, informal communication, and the human need for expressive language. Rather than focusing on exact meaning, its value lies in how it brings people together through tone and shared context. As language continues to evolve, expressions like yalla choy remind us that connection often matters more than precision.
Tech
UPERFECT 19-Inch 4K 144Hz Monitor: Big Performance in a Surprisingly Small Package
When it comes to monitors, bigger isn’t always better, especially if desk space is limited or you prefer a clean, compact setup. The UPERFECT 19-inch 4K 144Hz Monitor proves that you don’t need a massive screen to enjoy sharp visuals, smooth performance, and rich color quality. Designed for creators, professionals, and gamers alike, this compact display delivers impressive 4K clarity and high refresh performance in a size that fits almost anywhere.
Whether you’re editing high-resolution photos, working with detailed graphics, or enjoying fast-paced games, this monitor offers a polished visual experience that feels anything but small.
Incredible Detail Packed into a 19-Inch Screen
The first thing you’ll notice is the 4K UHD resolution (3840 × 2160). On a 19-inch screen, the pixel density is incredibly high, which means text looks razor-sharp, images appear crisp, and fine details really stand out. This makes everyday tasks feel cleaner and more refined, while creative work benefits from the added clarity.
Thanks to QLED panel technology, colors appear richer and more vibrant than on standard displays. The use of quantum dot enhancements helps produce more accurate hues and better contrast, giving images a lively and natural look, ideal for photo editing, video work, and visual design.
 Ultra-Smooth Performance with a 144Hz Refresh Rate
Ultra-Smooth Performance with a 144Hz Refresh Rate
Smoothness is another area where this monitor shines. The 144Hz refresh rate makes everything feel more responsive, from scrolling through documents to watching high-motion content. Compared to typical 60Hz displays, the difference is noticeable right away.
For gamers, the higher refresh rate brings smoother gameplay and more fluid motion, especially in fast-paced titles. When paired with adaptive sync support like FreeSync, screen tearing and stuttering are reduced, resulting in a more seamless visual experience—provided your system supports it.
Even outside of gaming, the smooth motion adds a premium feel to everyday use. Rich Colors and Strong Contrast for Creative Work
Color performance is a major strength of the UPERFECT 19-inch monitor. With 107.8% DCI-P3 color coverage, it displays a wider range of colors than standard sRGB screens. This makes it well-suited for creative professionals who need accurate color reproduction for tasks like digital illustration, photo retouching, or video editing.
The display also offers a solid 1200:1 contrast ratio, helping create deeper blacks and brighter highlights. Combined with wide 178-degree viewing angles, the image stays consistent and vibrant even when viewed from the side, useful when sharing content or collaborating with others.
HDR Support for Added Visual Depth
HDR support adds another layer of visual enhancement by improving contrast and brightness range. Highlights appear brighter, shadows retain more detail, and scenes feel more dynamic overall.
While HDR performance on compact monitors depends on brightness levels, its inclusion still enhances supported content and provides a noticeable improvement over standard displays when watching movies or reviewing high-quality visuals.
Sleek Design with Practical Adjustability
The monitor’s slim profile and minimal bezels give it a modern, professional look that fits neatly into almost any workspace. Despite its compact size, it doesn’t feel cramped or outdated.
A built-in adjustable stand allows you to tilt the screen for comfortable viewing, and when portability matters, the stand folds neatly into the back of the monitor. For users who prefer a customized setup, the monitor also supports VESA 75 × 75 mm mounting, making it easy to attach to monitor arms or desk mounts for improved ergonomics.
Flexible Connectivity for Modern Setups
Connectivity is simple and versatile. The monitor includes full-featured USB-C ports and a mini HDMI input, allowing it to work with laptops, desktop PCs, gaming consoles, tablets, and other compatible devices.
USB-C support is especially convenient, as it can deliver both video and power through a single cable when supported by the source device. This helps keep desks tidy and makes the monitor ideal for mobile or minimalist setups.
An additional USB-A OTG port allows you to connect peripherals like a keyboard or mouse directly through the monitor, which is especially useful for compact workstations or laptop-based setups.
Built-In Audio and Eye-Friendly Features
The UPERFECT 19-inch monitor includes dual built-in speakers, which are handy for video calls, casual media playback, and general use. While they won’t replace a dedicated sound system, they eliminate the need for external speakers in many situations.
To support long hours of use, the monitor also features low blue light technology, helping reduce eye strain during extended work sessions or long stretches of screen time. This makes it more comfortable for professionals and creators who spend hours in front of their displays.
Who This Monitor Is Best For
This monitor is a great fit for several types of users:
● Content creators and designers who need high resolution and wide color coverage ● Professionals and remote workers who value sharp text and smooth performance ● Gamers who want a compact display with high refresh rates
● Users with limited desk space looking for a powerful secondary monitor
Its 19-inch size makes it ideal as a secondary screen alongside a laptop or larger monitor, while still delivering premium performance on its own.
 Final Thoughts: Small Size, Serious Capability
Final Thoughts: Small Size, Serious Capability
The UPERFECT 19-inch 4K 144Hz Monitor shows just how much performance can be packed into a compact display. With stunning 4K clarity, vibrant QLED colors, smooth 144Hz motion, and flexible connectivity, it offers a rare combination of power and practicality.
Whether you’re building a space-efficient workstation, upgrading a laptop setup, or looking for a high-quality compact display for work and play, this monitor proves that you don’t need a big screen to enjoy a truly impressive visual experience.
Tech
Findutbes Explained: Meaning, Purpose, and Online Buzz

In the ever-evolving digital world, new and unfamiliar terms frequently surface, catching attention and sparking curiosity. One such term is findutbes. At first glance, it looks unusual, slightly familiar, and intentionally different. This mix of mystery and recognition is exactly why people search for it. In this detailed article, we’ll explore findutbes from every angle, uncovering its possible meaning, digital relevance, and why such words gain traction online.
Understanding the Term Findutbes
Findutbes is not a recognized English dictionary word, which instantly places it in the category of coined or invented terms. Words like this are often created for digital use, branding, or experimentation. Their meaning is not inherited from language history but shaped by how and where they are used.
Why Findutbes Looks Familiar Yet Different
One reason findutbes stands out is its resemblance to common digital terminology. It visually echoes words related to searching and online platforms, which creates instant familiarity. At the same time, the altered structure keeps it unique and searchable.
Possible Origins of Findutbes
Findutbes may be inspired by modern internet behavior, particularly searching, discovering, and exploring content. Many invented words are created by blending familiar sounds with unique spelling to produce a term that feels intuitive yet original.
Findutbes as a Digital Identity
In today’s online environment, a word can become a full identity. Findutbes could represent a website, tool, brand, username, or digital project. Because it carries no predefined meaning, its identity is completely flexible and creator-driven.
Why People Search for Findutbes
Most searches for findutbes are driven by curiosity. When users encounter an unfamiliar word in a link, post, or interface, their instinct is to search it. This natural curiosity fuels traffic and online interest.
SEO Value of the Keyword Findutbes
From an SEO perspective, findutbes is a powerful keyword. With little to no competition, it can rank easily in search engines. This makes it ideal for niche projects, experimental websites, or early-stage branding efforts.
Findutbes in Branding and Naming
Branding benefits greatly from originality. Findutbes is distinctive, easy to recognize, and unlikely to clash with existing trademarks. Once associated with a product or service, it can quickly develop strong brand recognition.
Psychological Impact of Invented Words
Invented words like findutbes activate curiosity in the brain. People naturally try to interpret or decode them. This mental engagement increases memorability, which is a major advantage in digital communication.
Findutbes and Internet Culture
Internet culture embraces creativity, randomness, and experimentation. Unusual words often gain popularity simply because they feel new. Findutbes fits naturally into this culture of innovation and digital exploration.
Could Findutbes Have a Hidden Meaning
Some coined words are inspired by multiple concepts merged into one. Findutbes could symbolically represent discovery, searching, or navigation. Its meaning can evolve depending on how it’s used.
Use of Findutbes in Creative Projects
Creative professionals often choose abstract names to allow interpretation. Findutbes could be used in tech projects, content platforms, storytelling, or digital tools where flexibility and originality matter.
Findutbes as a Placeholder Term
During development or testing, creators often use unique placeholders. Findutbes could serve this role, avoiding confusion with common words and making internal references clear and distinct.
How Findutbes Gains Meaning Over Time
Meaning grows through use. As findutbes is repeatedly associated with a specific function or idea, people begin to connect the word with that experience. Over time, it gains identity and recognition.
Flexibility of the Word Findutbes
One of the strongest advantages of findutbes is its adaptability. It can fit into technology, media, education, or entertainment without semantic restrictions, making it highly versatile.
Challenges of Using Findutbes
Originality sometimes requires explanation. Users may initially be unsure how to pronounce or interpret findutbes. Clear messaging and consistent branding help overcome this early confusion.
Findutbes in a Crowded Digital Space
Standing out online is difficult, but findutbes naturally draws attention. Its uncommon structure makes it easier to remember than generic terms, helping it cut through digital noise.
Why Unique Words Like Findutbes Matter Today
In a content-saturated world, originality is valuable. Words like findutbes represent a shift toward creative naming and self-defined meaning, where identity is built rather than borrowed.
Future Potential of Findutbes
As digital ecosystems grow, unique terms will become even more important. Findutbes has strong potential to evolve into a recognizable concept if used consistently across platforms.
Conclusion
Findutbes may not appear in traditional dictionaries, but it carries value through curiosity, originality, and digital relevance. It reflects how modern language is shaped by creativity and online behavior rather than strict rules. Whether used for branding, identity, or experimentation, findutbes proves that even invented words can hold meaning and potential in today’s connected world.
FAQs
What is findutbes?
Findutbes is a unique, invented term often linked to digital identity or online discovery.
Is findutbes an English word?
No, it is not a standard English word and appears to be a coined term.
Why do people search for findutbes?
People search it out of curiosity after encountering it online or in digital content.
Is findutbes good for SEO?
Yes, unique keywords like findutbes have low competition and strong ranking potential.
Can findutbes be used as a brand name?
Absolutely. Its originality and flexibility make it suitable for branding and creative projects.
-

 General3 months ago
General3 months agoAdonismale: The Ultimate Guide to the Modern Male Aesthetic
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoKirby Dedo: Meaning, Meme & Finger Puppet Trend
-

 Blog3 months ago
Blog3 months agoCandizi: Sweet Innovation for Modern Living
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoHealth Threetrees Com VN: Your Online Health Guide
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoInsoya: Next-Gen Soy Protein for Health & Sustainability
-

 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months agoComicsArmy: Your Complete Guide to Free Comics & Safe Reading
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoEchostreamhub — Stream Smarter
-

 Business & Finance3 months ago
Business & Finance3 months agoAwius: Earned-Wage Access, Uses & Benefits
